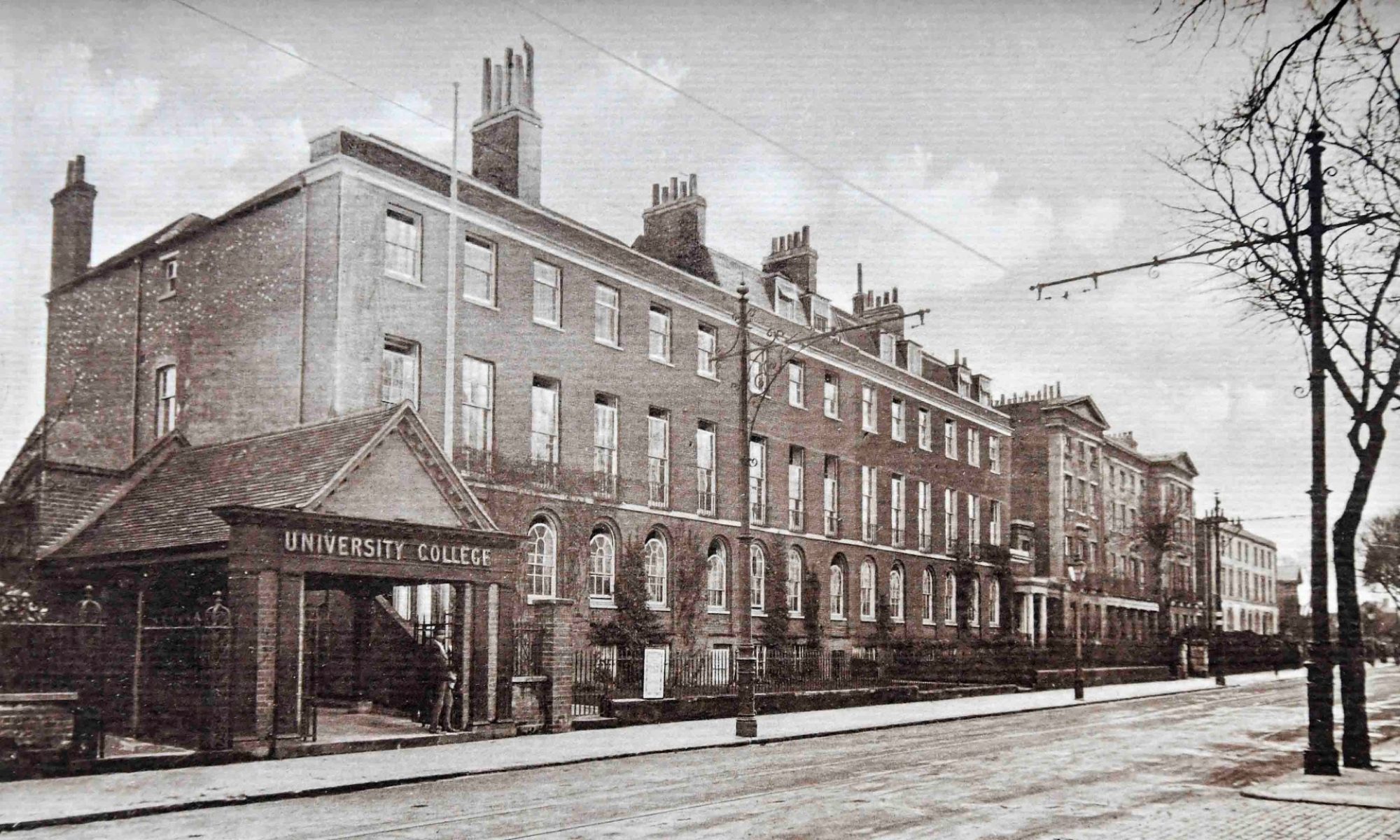
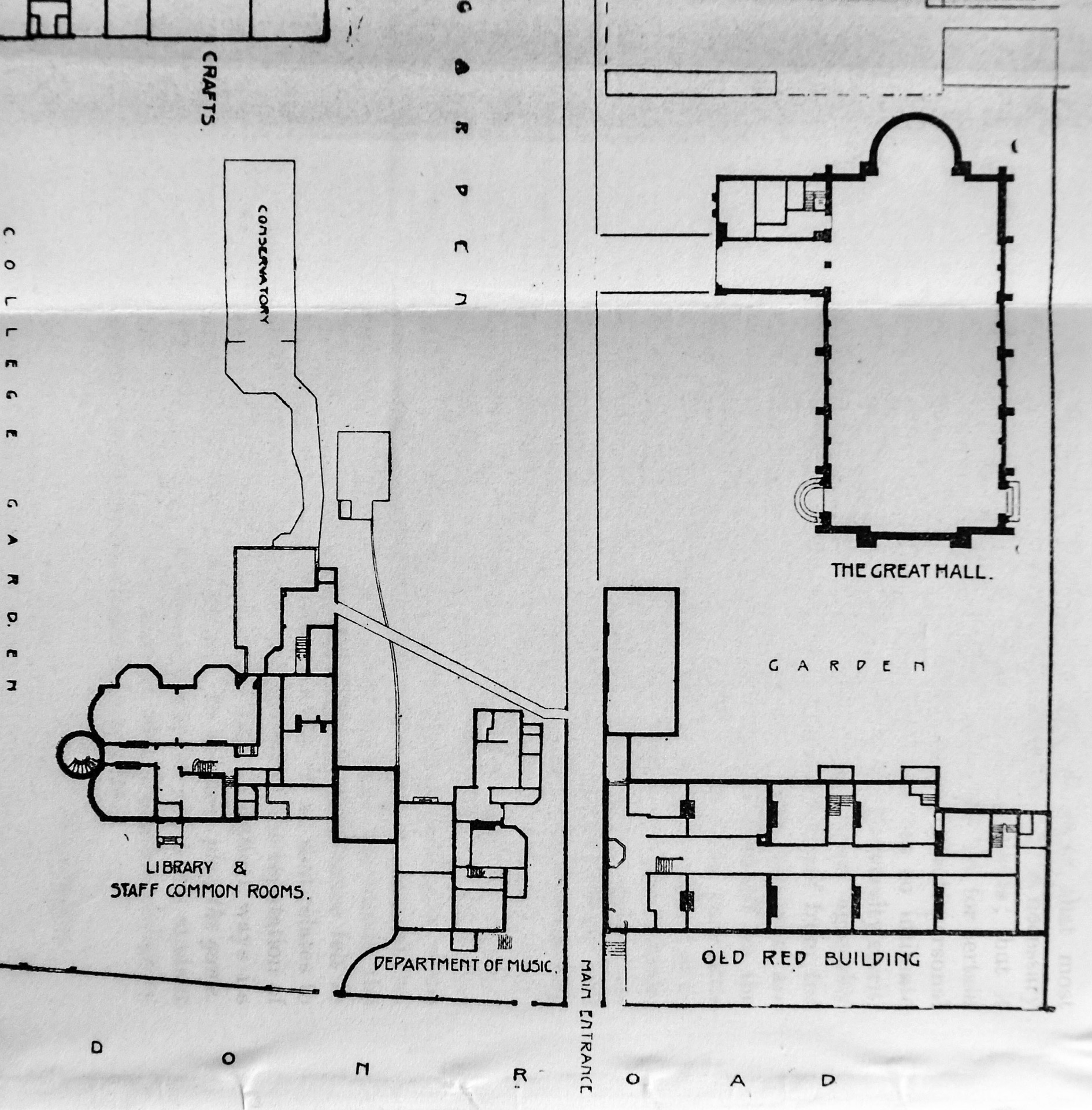
Lord Haldane, Secretary of State for War, performed the official opening of the Great Hall on the 27th October 1906. Most women were banned from attending for fear of disruption by suffragettes.
In an account of women’s suffrage, The Fabian Society and her own feminism, Edith Morley explains her position on acts of violence and illegality. While she disliked these on principle, she concedes that, without them, the struggle would have taken much longer. She points out that the violence was not one-sided and that women ‘suffered much worse than they inflicted or could inflict‘ (‘Reminiscences, p. 142).
Having dealt with serious matters of such significance, it seems strange that the following paragraph labels her exclusion from the opening ceremony of the Great Hall as one of ‘Several lighter incidents‘ instead of railing against the injustice of it. This is all she has to say on the topic:
‘In the thirty-nine years of my active connection with Reading College and University, once – and only once – was I absent on an important ceremonial occasion. This was when Lord Haldane, the Secretary for War, came to open the Hall in October 1906. He consented to officiate on condition that no woman, whether staff or student, was present at the ceremony; for no Minister at that time felt safe from suffragette interruptions.‘ (p. 142).
In fact, not all women were excluded, but those who did attend belonged to a certain level in society or were connected by marriage to the college – among others: Lady Wantage, Lady Saye, Lady Elliott, Mrs G. W. Palmer and Mrs Childs. A lowly English lecturer, or run-of-the mill members of staff or the student body were clearly too much of a threat!
The occasion was reported at length in The Times in an article that runs to well over 2,000 words. Haldane’s speech praised the College, the Hall and the new London Road site. Much of it was reproduced verbatim. Major themes were the inter-relationships between science and industry, wealth and the humanities. Speaking as a Minister of the State, he was concerned with the ‘Educational Needs of the Army‘.
Following his speech Haldane was presented with an inscribed silver inkstand by the architects, Messrs Ravenscroft and C. S, Smith. This was followed by a vote of thanks from the Principal, W. M. Childs, during which he announced to cheers that Lady Wantage had agreed to supply a Hall of Residence for male students.
This is how the article refers to the Great Hall:
‘The scheme of the new college embraces buildings both old and new. The principal feature of the new buildings is the great hall, the foundation-stone of which was laid by Lord Goschen last year. It was in this hall that the ceremony took place on Saturday. It is a handsome building, and will hold 1,000 people. A range of seven cloister buildings, which will later on be connected with the hall by other buildings, has also been erected.’
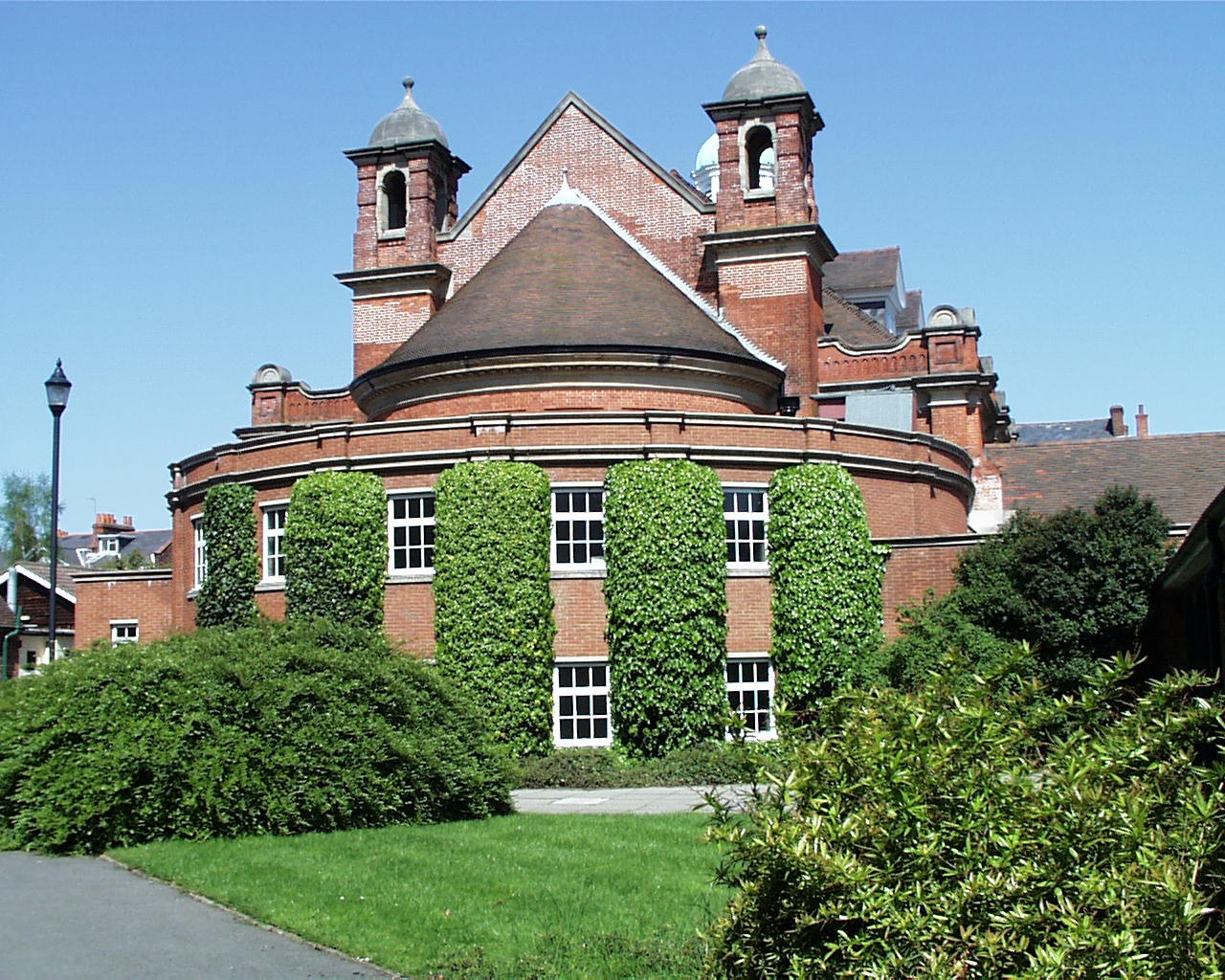

Two things are missing from The Times report – any mention of the exclusion of women, and Haldane’s predication that in fourteen years time the College would become the University of Reading.
Notes
1. Wantage Hall was opened in 1908 and provided accommodation for 76 male students. In their book ‘Reading’s Influential Women‘ Terry Dixon and Linda Saul inform us that Lady Harriet Wantage was ‘a prominent anti-suffragist, active as president of the North Berks Anti-Suffrage League.‘ Of Lady Wantage and Edith Morley they note that, ‘We assume they weren’t friends.‘ (p. 16).
2. This wasn’t Haldane’s only visit to the campus. He returned on 30 April 1909 in his official capacity as Secretary of State for War in order to address the male students about forming a College branch of the Officer Training Corps (more about this in a future post).
Sources
Childs, W. M. (1933). Making a university: an account of the university movement at Reading. London: J. M. Dent & Sons Ltd.
Dixon, T. & Saul, L. (2020). Reading’s influential women. Reading: Two Rivers Press.
Morley, E. J. (2016). Before and after: reminiscences of a working life (original text of 1944 edited by Barbara Morris). Reading: Two Rivers Press.
The Reading University College Review, Vol. I, 1908-9, pp. 154-7.
University College Reading, Annual Report and Accounts, 1905-6.
University College, Reading. Calendar, 1910-11.
University College, Reading. Speech by Mr Haldane. (1906, October 29). The Times, p. 3.
University College Reading (1907). Students’ handbook. First issue: 1907-8. Reading: UCR.