In December 1915, the College Review reported a speech about opportunities for women in which University College, Reading was singled out for a special pat on the back.
The speech was given by Sara Burstall, Head of the Manchester High School for Girls from 1898 to 1924, and the second headmistress of the independent school that had been founded in 1874. As can be seen from the text of her speech below, she was a champion of women’s education. She was also a strong supporter of women’s suffrage. Details of her life and career can be found here in the school’s digital archives.

In her address, Miss Burstall stressed that any reduction in the government grant would have a direct impact on women students in the newer universities . She continued:
‘In these centres of higher education women enjoy full rights, and to maintain and increase the efficiency of these institutions is one of the most important needs of women’s education. We have only to study what is being done for women at University College, Reading, to see an example of what is needed, and what deserves public support and credit.’ (pp, 20-21).
These words raise three questions. What was it about Reading that stood out? What was life really like for women students? How did Sara Burstall know so much about University College, Reading?
What was it about Reading that stood out?
Several factors may be relevant:
- University College, Reading was a pioneer in the provision of student hostels and halls of residence, especially for female students. Even as early as 1907, two such hostels provided for 80 women (Childs, 1933). It seems to have been assumed that women from outside the area would be provided with accommodation — in the mid-1920s, the novelist Elspeth Huxley had no choice but to accept an ‘approved lodging’ in a hostel, having applied too late for a place in a hall of residence.
- Wardens of women’s halls and hostels, for example Mary Bolam at St Andrew’s, were very protective of their charges and were concerned with both their personal and academic well-being.
- Universities and colleges that established a senior position dedicated to the welfare and discipline of female students tended to be favoured by parents and the headteachers of girls’ schools (Dyhouse, 1995). In 1915 this post, officially known as the Censor of Women Students, was occupied by Lucy Ashcroft, herself a former Maths teacher in high schools for girls.
- The College already had a high proportion of women students, especially in subjects such as dairying, teacher education and horticulture. The trend towards equal numbers of men and women would continue once the College had become a University in 1926 (see Dyhouse, 2006).
- It was claimed that women and men at Reading had equal access to all classes and College societies (Dyhouse, 1995).
- In 1908 Edith Morley had been made Professor of English Language, the first woman in the UK to obtain a chair at a university or a college of similar academic standing.
I wondered whether Reading offered funding that was exclusive to women. Thanks to the diligence of Professor Edith Morley, this information is readily available: Morley’s edited volume ‘Women workers in seven professions’ (1914) contains a table listing details of the first degrees at all universities and university colleges in the UK, together with the availability of scholarships, bursaries and prizes. Those reserved for women are clearly identified.
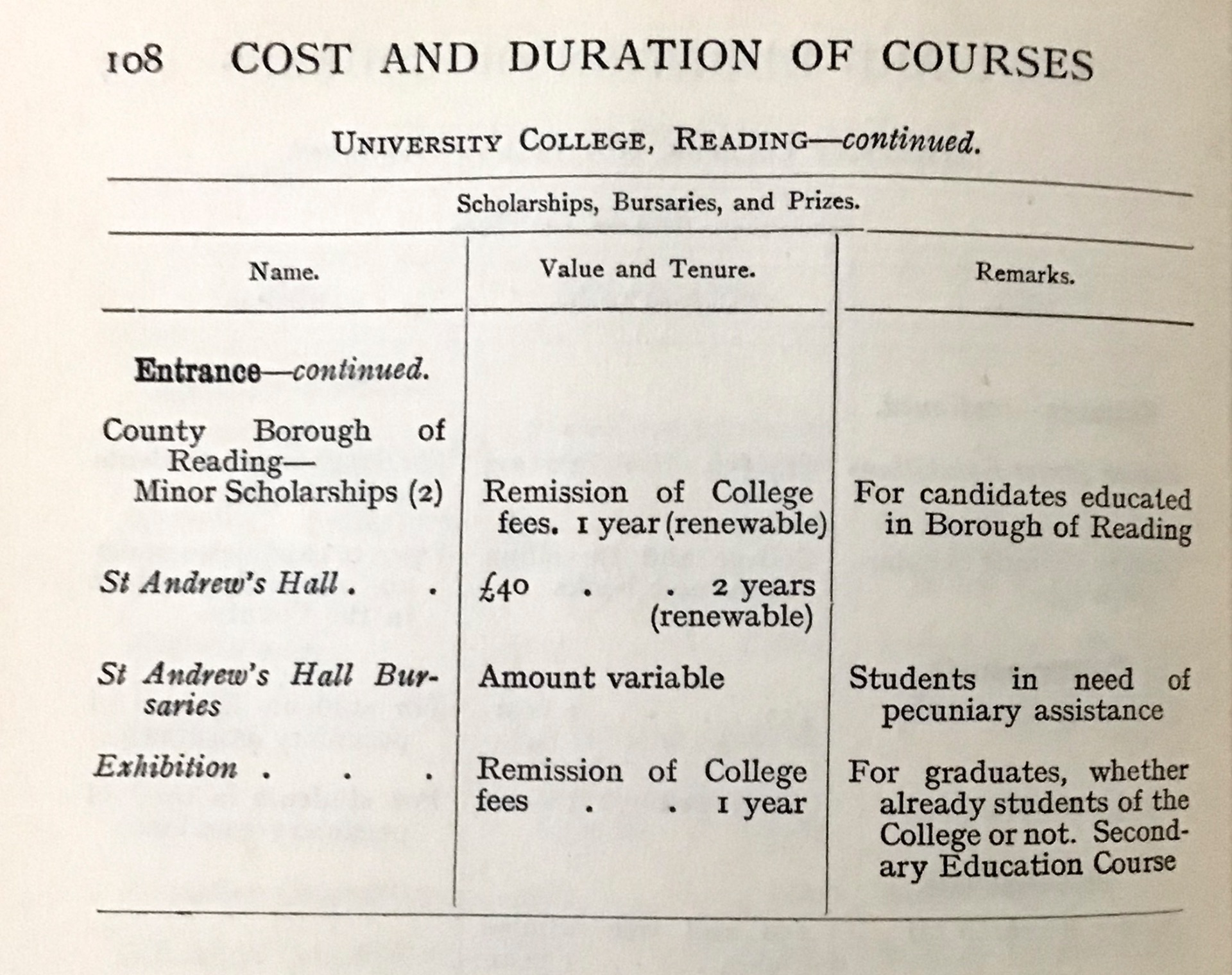
Reading was indeed one of the institutions that set aside financial assistance for women, particularly for students in St Andrew’s Hall. However, these were no more generous or numerous than those at many other institutions.
What Was life really like for women students?
With regard to the bullet points above, Reading seems to compare well with other colleges and universities. I have found no accounts of women having to pay for chaperones in order to attend classes, or being unable to attend meetings or access the library such as those reported In Carol Dyhouse’s (1995) history of women in higher education.
Nevertheless, as Dyhouse points out, there was a great deal of separation between male and female students at Reading, as well as a tendency to study different subjects. There were separate students’ unions, common rooms, sporting activities and separate rules of discipline in halls and elsewhere that often placed tighter restrictions on women than on men.
Such divisions were reported by no less a figure than Albert Wolters, the founder of Reading’s Psychology Department. He recalled that, when he was an education student in 1902, the men were outnumbered by two to one, and that:
‘The present-day student would be astonished at the way in which the men and women held to their own communities … We, the small body of men, were completely integrated, and we dominated the student body ruthlessly and objectionably. But at the end of the year we, who would have been the new oligarchy, saw the folly of our ways and threw our strength into the foundation of the Men Students’ Union..” (Wolters, 1949, p. 18).
The pages of Tamesis, the College Magazine, bear witness to the patronising attitudes, mockery and even contempt to which women were subjected. Some of the articles are quite offensive, but the women showed themselves quite capable of responding in kind.
Probably the most repugnant attack on the female student body was contained in a spoof edition of Tamesis that was compiled (presumably by male students) in 1927. This so-called ‘Scandal Supplement’ with its feeble and sometimes incomprehensible humour includes a poem titled ‘Some Views on Women’ that is declared to be the leading article and dominates the front page. The image below gives an indication of the tone of its content.

What was Sara Burstall’s connection to Reading?
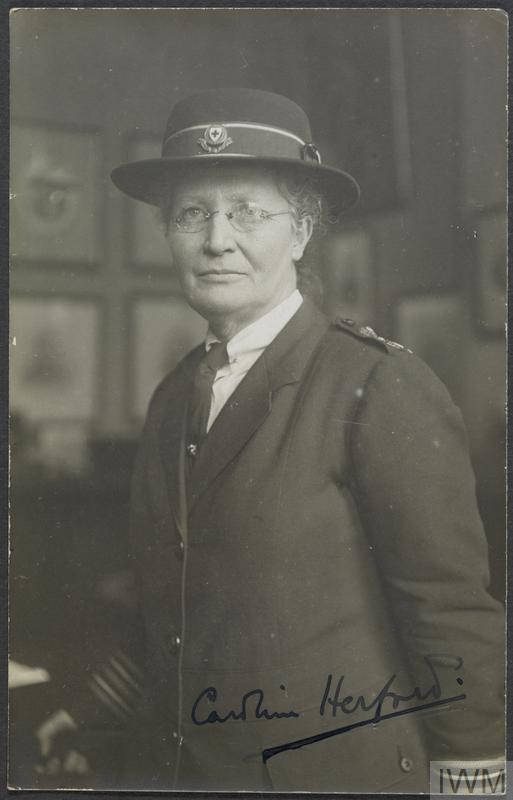
I can’t be certain, but I believe the link to be Caroline Herford who has been the subject of two previous posts on this blog (her portrait can be seen below). Born and educated in Manchester and a former headteacher, Herford became Reading’s first Lecturer in Secondary Education in 1909. She left after only six terms, but the notice of her resignation in the College Review is full of praise for her impact on the college and for her expertise and professionalism. She returned to her roots in Manchester in 1910 for a post as Lecturer in Secondary Education at the University where it is likely that she came into contact with Sara Burstall.
It is also likely that they already knew each other as headteachers — when Herford had been the Head of Lady Barn House School, the period of her headship overlapped with that of Burstall: Herford’s from 1886 to 1907, and Burstall’s from 1898 to 1924.
Manchester High School for Girls would almost certainly have been a destination for at least some of the girls leaving Lady Barn House, just as it still was in September 2022!
Archivists at the Manchester High School for Girls have found three mentions of the Herfords in their paper records. The first refers to May Herford who taught Classics from 1915 to 1916; the second is Charles Herford, Caroline’s cousin, who was Professor of English at Manchester University and whose tribute to a former teacher at the school was published in the School Magazine in 1917; the third refers again to Charles Herford who, as well as Sara Burstall, attended the funeral of Margaret Gaskell (daughter of Elizabeth Gaskell), one of the school’s founders. I think, therefore, that we can be confident of a connection between the school and the Herford family.
A third point of contact could have been the Lancashire Red Cross during World War I. According to the digital archives of Manchester High School for Girls, Sara Burstall was on holiday when the war broke out in 1914, but returned immediately and, with advice from the Red Cross, set up a Centre for making clothes and hospital supplies at the school.
At the same time, and in addition to her academic duties, Caroline Herford was a Commandant of the Lancashire Red Cross, a position she held until 1918 and for which she was awarded the MBE. It’s sheer speculation, of course, but could it have been Caroline Herford who advised Sara Burstall on establishing the centre at the High School?

Note
The back of the photograph of Caroline Herford contains the following handwritten details of the work of her students and colleagues in Manchester:
‘Squads of University Students met Ambulance Trains at all hours of the night, and gave hot tea & coffee to the wounded, which were prepared in the Porters’ Room. Between 11 May 1915 and 11 May 1919 they met & [illegible word] 866 trains.’
Thanks
To the Imperial War Museum for permission to use the image of Caroline Herford.
A very special thanks to Gwen Hobson and Pam Roberts, archivists at the Manchester High School for Girls who searched School Magazines, School Reports, Governors’ Minutes, letters and newspaper articles for references to the Herford family and to Sara Burstall’s talk.
Another special thank-you to Dan Slade, Deputy Head of Lady Barn House School, for further information and documentation about the Herfords.
Sources
Childs, W. M. (1933). Making a university: an account of the university movement at Reading. London: J. M. Dent & Sons Ltd.
Dyhouse, C. (1995). No distinction of sex? Women in British universities, 1870-1939. London: UCL Press.
Dyhouse, C. (2006). Students: a gendered history. Abingdon: Routledge.
Herford, C. H. (1917). Annie Adamson. In S. A. Burstall (Ed.), Memorial Number of the Manchester High School for Girls (pp. 18-22) [Originally published in the Modern Language Quarterly].
Huxley, E. (1968). Love among the daughters. London: Chatto & Windus.
Morley, E. J. (Ed.). (2014). Women workers in seven professions: a survey of their economic conditions and prospects (pp. 11-24). London: Routledge. [Edited for the Studies Committee of the Fabian Women’s Group].
Manchester High School for Girls Digital Archives: https://www.mhsgarchive.org
Oxford University Press (2004). Oxford dictionary of national biography. Oxford: OUP.
Reading College Magazine, 1901-2.Tamesis, Winter Term, Vol II, 1901, pp. 11-12 [anonymous criticism of women’s hockey].
Tamesis, Spring Term, Vol III, 1901, p. 32 [anonymous counter-attack by ‘A Hockey Player’].
Tamesis Scandal Supplement, Reading, June 1927, University of Reading Special Collections.
The Reading University College Review, Dec 1910, Vol III, No. 7, p.24. [Notice of Herford’s resignation].
The Reading University College Review, Dec. 1915, Vol. VIII, No. 22, pp. 20-21. [Miss Burstall on women’s education].
Wolters, A. W. (1949). Early days. In H. C. Barnard (Ed.), The Education Department through fifty years (pp. 18-20). Reading: University of Reading.







