Radiative Performance Comparison of 10 Tree Species Planted in the UK

Tree Species Shown (Left to Right)
(1) Horse Chestnut, London Plane
(2) Beech, Large-leaved lime, English Oak, Field Maple
(3) Autumn Blaze, Fastigiage hornbeam
(4) Silver Birch
(5) Giant Sequoia
- Visually dense tree measuring patches without visible gaps in crown foliage
and concave crown contours in the viewing vision were selected - All trees measured are young adult to mature adult trees
- Sunlit side of trees are measured
- Solar Altitude = 45°C
Results:
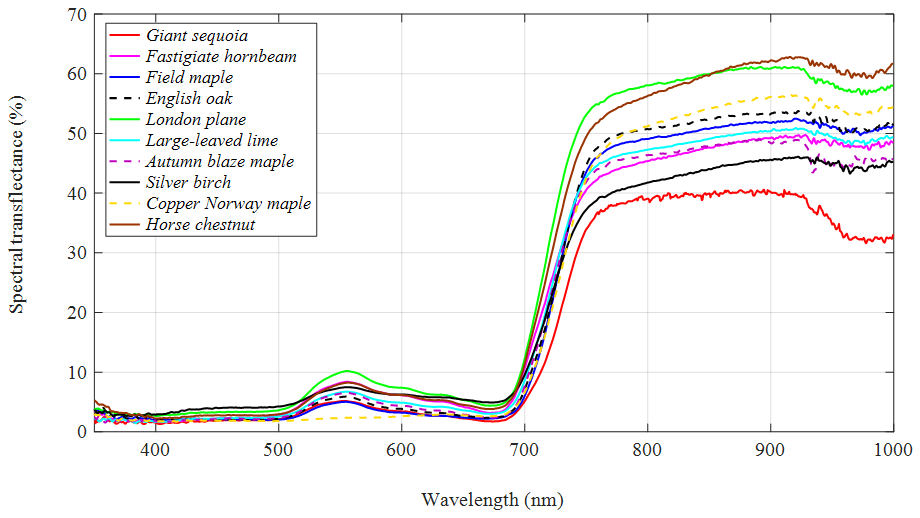
- Mean leaf reflectance spectra of various tree species have a minor
difference between each other - At the tree crown level, it was indicated that tree species with large-sized leaves, lead to maximum radiative performance levels, followed by the tree species with moderate-sized leaves
- Giant Sequoia has the minimum radiative performance level, mainly due to its small needle leaves
“Difference of the infrared radiative performance levels between tree species strongly depends on leaf size if visually dense foliage (no obvious gaps in foliage and no concave shapes) is observed on the tree crown contours”

