Written By Louise Cowan, Trainee Liaison Librarian
This month sees the anniversary of the first European ship landing in Eastern Australia. Led by
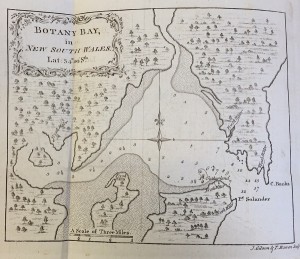
British explorer, James Cook, the crew of the H.M.S. Endeavour reached Botany Bay at the end of April 1770.
The Special Collections Library has a number of volumes on the voyages of Captain Cook but the narrative in “An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of his Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successfully performed by Commodore Bryon, Captain Carteret, Captain Wallis and Captain Cook in the Dolphin, the Swallow and the Endeavour,” by John Hawkesworth (1773), is perhaps one of the most detailed. The reason for this is clearly explained by Hawkesworth himself in the preface to volume II:
The papers of Captain Cook contained a very particular account of all the nautical incidents of the voyage, and a very minute description of the figure and extent of the countries he visited […] But in the papers of Mr. Banks, I found a great variety of incidents which had not come under the notice of Captain Cook…
Mr. Banks, or Sir Joseph Banks, was an explorer, naturalist and president of the Royal Society who accompanied Cook as the lead scientist on the voyage. Hawkesworth combines the journals of both Cook and Banks to give a thorough and detailed survey of the journey.
As the first scientific expedition to the Pacific (Villiers, 2016) the voyage had set out with two main goals; the first was to observe the transit of the planet Venus across the Sun on 3 June 1769 at Otaheite (Tahiti):
The whole passage of the planet Venus over the Sun’s disk was observed with great advantage by Mr Green, Dr Solander, and myself.
The second aim was to find the theoretical southern continent ‘Terra Australis’. So, on leaving Tahiti,
Cook opted for a route divergent to his predecessors, sailing south and southwest, (Villiers, 2016), a decision which led him to the discovery of New Zealand. He and his crew spent several months exploring and charting the island before sailing on to Australia, where they made their first landing at Botany Bay:
The place the ship had anchored was abreast of a small village, consisting of about six or eight houses […] we intended to land where we saw the people, and began to hope that as they had so little regarded the ship’s coming into the bay, they would as little regard our coming on shore: in this however, we were disappointed; for as soon as we approached the rocks, two of the men came down upon them to dispute our landing, and the rest ran away.
They stayed at Botany Bay for eight days, and despite several brief encounters, the Captain and his crew were unable to make significant contact with the Aboriginal people, who were unsettled by the new arrivals, often throwing lances at the crew or running away in fear:
A lance was immediately thrown at him out of the wood, which narrowly missed him. When the Indians saw that the weapon had not taken effect, they ran away.
Although Cook and his crew were unable to form any fruitful relationships with the people they encountered on this occasion, Mr Banks and his assistant, Dr. Solander, a Swedish botanist, were able to collect a wealth of botanical materials, earning the Bay its name:
The great quantity of plants which Mr. Banks and Dr. Solander collected in this place induced me to give it the name of BOTANY BAY.
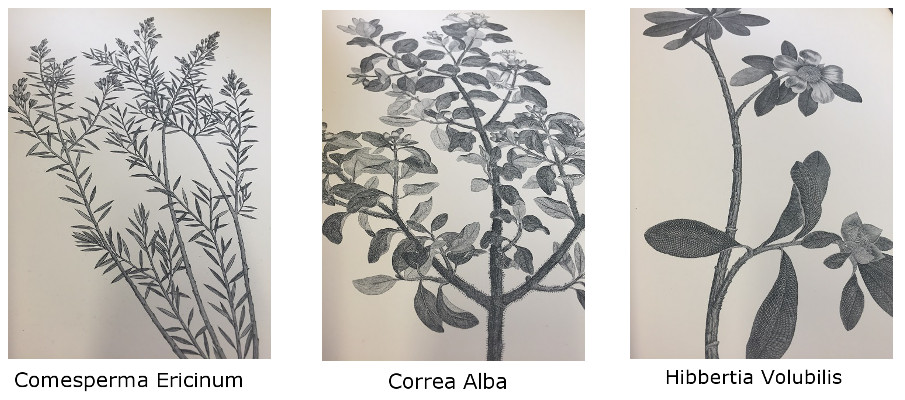
The Special Collections Library holds a copy of ‘Illustrations of the Botany of Captain Cook’s Voyage Round the World in H.M.S. ENDEAVOUR in 1768-71’ by Sir Joseph Banks and Dr. Daniel Solander, (1900). The two part work contains beautiful engravings of a number of plant specimens, including some of those Banks and Solander found at Botany Bay:
The success of the expedition for Sir Joseph Banks and his team helped to establish the tradition of sending scientists on naval voyages and inspired interest not only in the discovery of new lands but in the possibility of new discoveries in science, (Villiers, 2016).
Following this journey, Cook continued his epic sea voyages, his explorations eventually showing that, “a real Terra Australis existed only in the landmasses of Australia, New Zealand, and whatever land might remain frozen beyond the ice rim of Antarctica,” (Villiers, 2016).
Sources:
Hawkesworth, J. (1773) An Account of the Voyages Undertaken by the Order of his Present Majesty for Making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere and Successfully performed by Commodore Bryon, Captain Carteret, Captain Wallis and Captain Cook in the Dolphin, the Swallow and the Endeavour. [Overstone Shelf 26 E – Available on request]
Banks, J., Solander, D (1900) Illustrations of the Botany of Captain Cook’s Voyage Round the World in H.M.S. ENDEAVOUR in 1768-71’ [Reserve Middle Folio 581.944 BAN – Available on request]
Alan John Villiers (2016) James Cook. Britannica Academic. Available from: http://academic.eb.com.idpproxy.reading.ac.uk/EBchecked/topic/135983/James-Cook
Sir Joseph Banks 2016. Britannica Academic. Retrieved 27 April, 2016, from http://academic.eb.com.idpproxy.reading.ac.uk/EBchecked/topic/52035/Sir-Joseph-Banks